Wet Cupping Therapy
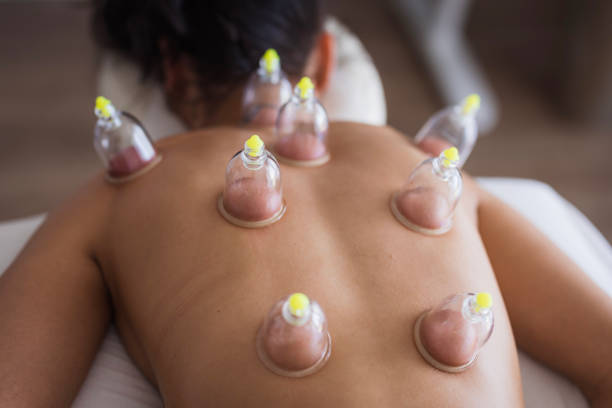
Wet Cupping Therapy
Wet cupping therapy, also known as Hijama, is a traditional medical practice where small incisions are made on the skin after creating suction, allowing for the removal of "stagnant" or "impure" blood. This therapy combines elements of both dry cupping and a controlled bloodletting process. It has roots in ancient practices across various cultures and is widely used in traditional medicine systems.
How It Works:
- Preparation:
- The skin is cleaned and sterilized to prevent infection.
- Cups are placed on specific areas, often determined by the practitioner based on the condition being treated.
- Suction Phase:
- Suction is created using heat or vacuum pumps to pull the skin into the cup.
- This increases blood flow to the area, loosens tissues, and prepares the body for the next step.
- Incisions:
- After removing the cups, tiny superficial incisions are made on the skin using a sterile scalpel.
- Blood Extraction:
- The cups are reapplied, and suction draws out a small amount of blood. This process is thought to remove toxins, stagnant blood, and impurities from the body.
- Post-Treatment Care:
- The area is cleaned again, and antiseptics or healing ointments are applied.
- Bandages are placed to protect the skin and promote healing.
